
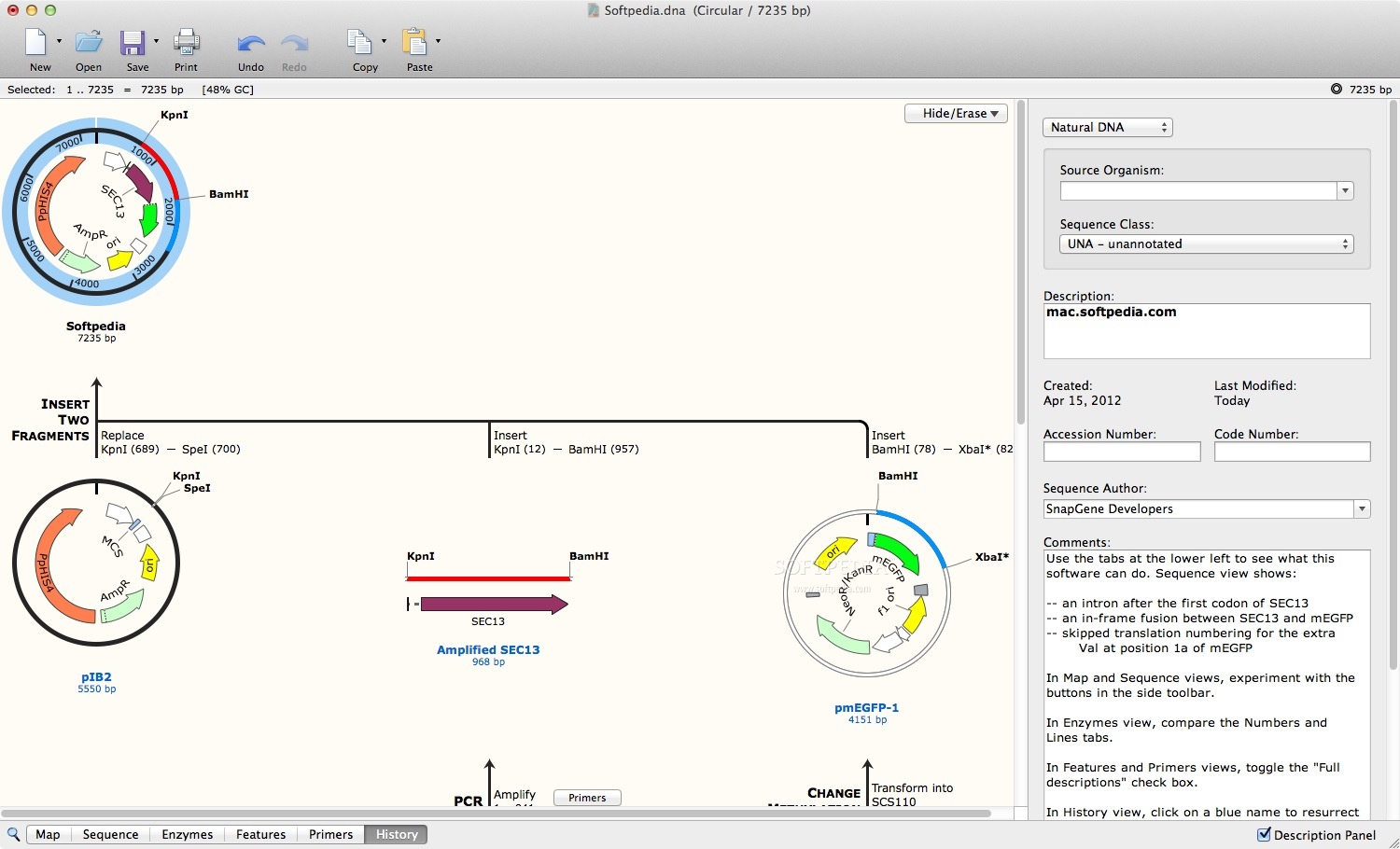
Fixed an issue with Geneious file import where features in protein sequences could erronously be translated.Use the default file format specified in Preferences when exporting alignments.Fixed an issue where Ready to Clone was still shown after adding or removing a fragment, even if cloning was no longer possible.Fixed an issue where selected codons were not always shown using a white foreground in Sequence view.
Snapgene viewer windows#
Fixed an issue where some windows omitted the title bar on Windows. Fixed an issue where cloning dialogs could get stuck generating the product. Fixed or improved various links to pages. Improved mouse pointer shape when over links in Collection windows. Fixed an issue that prevented the Enzymes view "Select Range" context menu command from working. Improved text spacing after punctuation characters on macOS.  Ensured the fragment list in cloning dialogs continue to refresh when either enzyme is manually cleared. Fixed issues with opening some GenBank files. Various textual and layout enhancements. Provide a cancel option when a message is shown indicating an unknown or not installed custom feature type must be addressed before proceeding with editing or duplicating one or more features. Improved the detection and simplified the display of primer hybridizations with 3' overhangs. Ladder fragment lengths are now displayed in the fragment list in agarose gels. Added "Synthetic Protein" and "Unknown" options for the Source attribute in the description panel. Enabled customization of content exported to GenBank including LOCUS field identifier and feature export options. Native support for Apple Silicon machines.
Ensured the fragment list in cloning dialogs continue to refresh when either enzyme is manually cleared. Fixed issues with opening some GenBank files. Various textual and layout enhancements. Provide a cancel option when a message is shown indicating an unknown or not installed custom feature type must be addressed before proceeding with editing or duplicating one or more features. Improved the detection and simplified the display of primer hybridizations with 3' overhangs. Ladder fragment lengths are now displayed in the fragment list in agarose gels. Added "Synthetic Protein" and "Unknown" options for the Source attribute in the description panel. Enabled customization of content exported to GenBank including LOCUS field identifier and feature export options. Native support for Apple Silicon machines. 
 Added support for Dark mode, automatically using the OS settings for macOS and Windows. Structures calculated using the ViennaRNA package New Secondary Structure view tab for single stranded RNA sequences. New Golden Gate Assembly simulation tool, either using existing Type IIS enzymes or through automated primer and overhang design. Trace files are stored in proprietary formats, such as those of ABI, or public formats such as SCF. Therefore, an increasing number of people need to check the evidence for individual DNA sequences by inspecting the chromatograms (more commonly known as trace files) from which the base calls were deduced. With the sequencing of the human genome and new era of molecular, one can only expect the use of DNA sequencing to increase. Currently, sequencing is used to identify microbial drug resistance mutations, cancer predisposition, somatic mutations, and genetic diseases. These developments have made sequencing easier to perform and therefore more widely used. Major advances in DNA sequencing include the development of automated sequencers, discovery of fluorescent terminator chemistry, and cycle sequencing. TraceEdit is freely available and designed to operate on Windows and UNIX platforms.DNA sequencing has been the standard against which other types of DNA testing is compared. Incorrect base calls can be edited and saved. TraceEdit displays the chromatogram files from Applied Biosystems automated sequencers and files in the Staden SCF format. Ridom TraceEdit is a cross-platform graphical DNA trace viewer and editor.
Added support for Dark mode, automatically using the OS settings for macOS and Windows. Structures calculated using the ViennaRNA package New Secondary Structure view tab for single stranded RNA sequences. New Golden Gate Assembly simulation tool, either using existing Type IIS enzymes or through automated primer and overhang design. Trace files are stored in proprietary formats, such as those of ABI, or public formats such as SCF. Therefore, an increasing number of people need to check the evidence for individual DNA sequences by inspecting the chromatograms (more commonly known as trace files) from which the base calls were deduced. With the sequencing of the human genome and new era of molecular, one can only expect the use of DNA sequencing to increase. Currently, sequencing is used to identify microbial drug resistance mutations, cancer predisposition, somatic mutations, and genetic diseases. These developments have made sequencing easier to perform and therefore more widely used. Major advances in DNA sequencing include the development of automated sequencers, discovery of fluorescent terminator chemistry, and cycle sequencing. TraceEdit is freely available and designed to operate on Windows and UNIX platforms.DNA sequencing has been the standard against which other types of DNA testing is compared. Incorrect base calls can be edited and saved. TraceEdit displays the chromatogram files from Applied Biosystems automated sequencers and files in the Staden SCF format. Ridom TraceEdit is a cross-platform graphical DNA trace viewer and editor.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
